TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol a communications standard that enables application
programs and computing devices to exchange messages over a network. It is designed to send packets
across the internet and ensure the successful delivery of data and messages over networks.
TCP organizes data so that it can be transmitted between a server and a client. It guarantees the
integrity of the data being communicated over a network. Before it transmits data, TCP establishes a
connection between a source and its destination, which it ensures remains live until communication
begins. It then breaks large amounts of data into smaller packets, while ensuring data integrity is
in place throughout the process.
As a result, high-level protocols that need to transmit data all use TCP Protocol.
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the method for sending data from one device to another across the
internet. Every device has an IP address that uniquely identifies it and enables it to communicate
with and exchange data with other devices connected to the internet.
IP is responsible for defining how applications and devices exchange packets of data with each
other. It is the principal communications protocol responsible for the formats and rules for
exchanging data and messages between computers on a single network or several internet-connected
networks. It does this through the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP), a group of communications
protocols that are split into four abstraction layers.
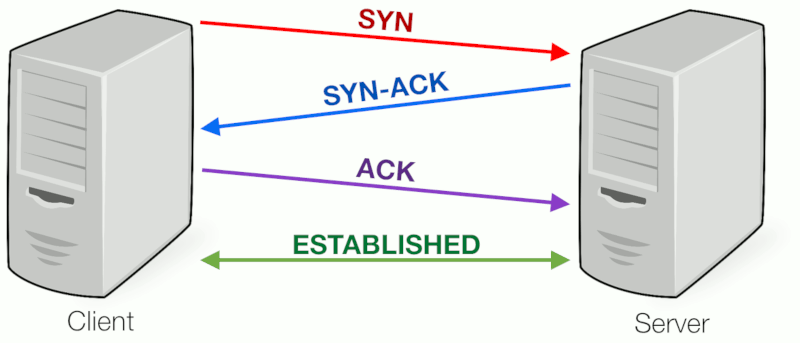
TCP, a connection is established and a 3-way handshake is made. First, the source send an SYN
“initial request” packet to the target server in order to start the dialogue. Then the target server
then sends a SYN-ACK packet to agree to the process. Lastly, the source sends an ACK packet to the
target to confirm the process, after which the message contents can be sent.