A socket is one endpoint of a two-way communication link between two programs
running on the network. The socket is bound to a port number so that the TCP layer can identify the
application that data is destined to be sent.
Sockets provide the communication mechanism between two computers using TCP. A client program
creates a socket on its end of the communication and attempts to connect that socket to a server.
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol provides reliable communication between the sender and
receiver. TCP is used along with the Internet Protocol referred as TCP/IP.
UDP: User Datagram Protocol provides a connection-less protocol service by allowing packet
of data to be transferred along two or more nodes
Before exchanging data, computers must establish a link that is for connection-oriented protocols.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is the only option for connectionless protocol. For exchanging data TCP
is used which is connection-oriented protocol.
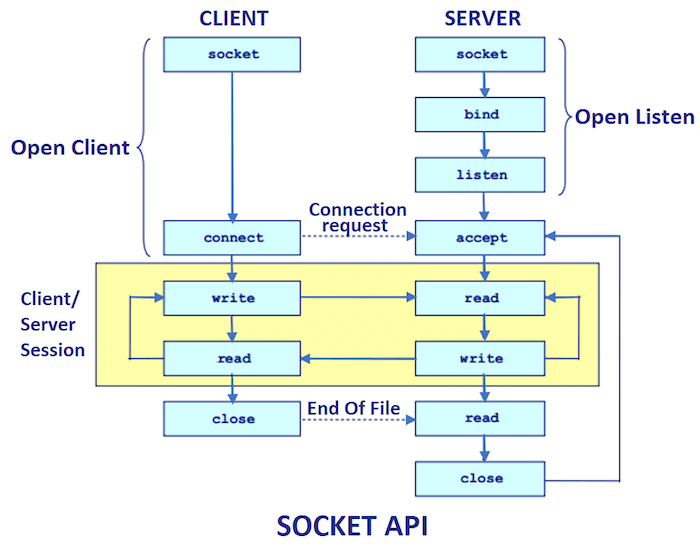
Client socket programming, the client will first wait for the server to start. Once the server is up and running, it will send the requests to the server. After that, the client will wait for the response from the server. Socket s=new Socket("localhost",6666);
Server socket programming,,the server will instantiate its object and wait for the client request. Once the client sends the request, the server will communicate back with the response. ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(6666); Socket s=ss.accept();
Server Side
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(6666);
Socket s=ss.accept();//establishes connection
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
String str=(String)dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("message= "+str);
ss.close();
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
}
}
Client Side
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
Socket s=new Socket("localhost",6666);
DataOutputStream dout=new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
dout.writeUTF("Hello Server");
dout.flush();
dout.close();
s.close();
}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e);}
}
}